18 Legislative Process
It is important to understand how legislation is made. This knowledge will assist you in research tasks such as:
- tracking proposed legislation prior to enactment
- locating parliamentary documents needed in statutory interpretation.
Commonwealth legislative process
The passage of a Bill through Parliament is similar in most common law jurisdictions. The Commonwealth process is as follows:
- introduced to Parliament by the Minister responsible (may be introduced in either the House of Representatives or the Senate)
- read for the first time
- read for a second time – explanatory speech and debate
- proceeds to Committee stage (optional) — consideration and report from the relevant committee
- moves to consideration in detail (optional) — Bill considered clause by clause (amendments can be made at this time)
- read for the third time — agreed to
- considered by, and amendments agreed to, by the other House (bicameral Parliament)
- receives Royal Assent — and is enacted.
The Parliament of Australia’s Infosheet 7 Making Laws describes how bills are proposed, considered and passed at a federal level.
Making a law in the Australian Parliament is a fact sheet explaining the law-making process in the Australian Parliament.
The legislative process in other jurisdictions
The passage of a Bill through parliament is similar in most common law jurisdictions. See further reading on the jurisdiction of your choice below:
- Factsheet No. 6 – Making Laws (Parliament of New South Wales)
- How Parliament Works (Parliament of South Australia)
- How Laws are made (Parliament of Tasmania)
- Learn how Parliament works (Parliament of Western Australia)
- How laws are made (Parliament of Victoria)
- How laws are made (Legislative Assembly for the Australian Capital Territory)
- Information papers (Legislative Assembly for the Northern Territory)
One noteworthy difference is that the Queensland Parliament has abolished its Legislative Council and now use a unicameral (or one chamber) system. The diagram below reflects the typical passage of a Bill through the Queensland Parliament rather than the legislative process of a Parliament with two houses.
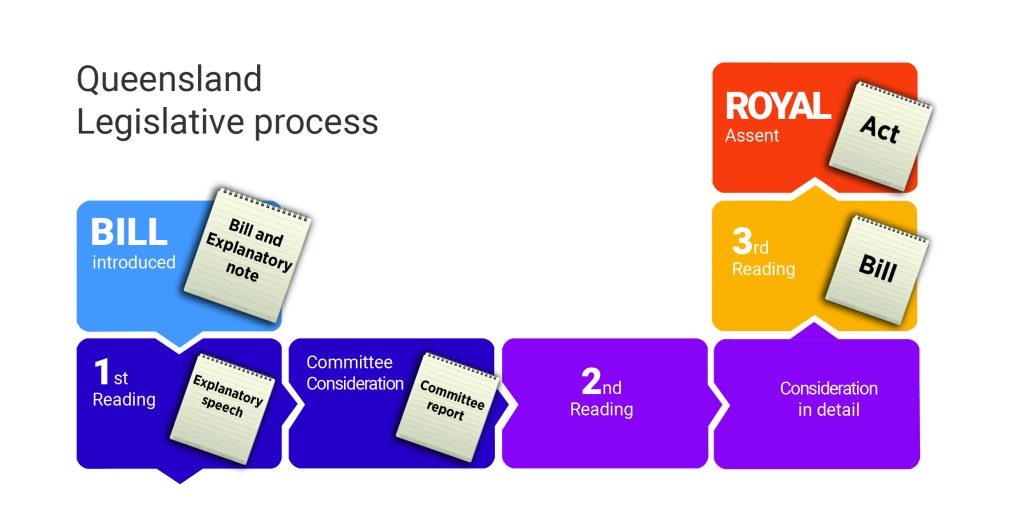
Read more about Queensland’s parliamentary process in the Queensland Legislation Handbook or Queensland Parliament’s Factsheet 3.6 (PDF, 269KB).

