4.5.1 Reviewing the Literature
Faith Alele and Bunmi Malau-Aduli
It is very important to have a thorough understanding of published literature in an area of study because strong scholarship is a prerequisite for sound research.1
According to Fink (2019), a literature review is a systematic, explicit, and reproducible procedure for identifying, evaluating and synthesising the existing body of recorded and completed work produced by researchers.2
The role of literature searches and reviews was discussed and highlighted as one of the ways to develop a research idea and to identify gaps that could lead to the development of a research question.3 A novice researcher should critically review published articles and undertake a thorough search of the published literature in the fields relevant to the research issue.3 Performing a search of the literature requires an understanding of the different types of research literature.
Types of research literature
There are two main types of literature- primary research literature and secondary research literature. Literature that reports primary research is original research published in peer-reviewed journals. These could include case studies, case series, cross-sectional, cohort, case-control and experimental studies.
Question
Distinguish between a case study, a cohort study and an experimental study.
Primary literature also includes reports, congress papers, dissertations and preprints. This type of research could be identified from databases such as Medline/PubMed, CINAHL (Cumulative Index of Nursing and Allied Health Literature), Emcare, Embase, Google Scholar, Scopus, Web of Science, or PsycINFO. The other type, which is secondary literature, reports findings synthesised from primary sources and includes systematic reviews (review of primary research), meta-analysis (a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple quantitative studies) or meta-synthesis (synthesis of multiple qualitative studies).
Types of literature reviews
A literature review is a critical evaluation and analysis of existing literature on a particular topic or research question.
Literature reviews can be broadly grouped into seven families – traditional literature reviews, systematic reviews, review of reviews, rapid reviews, qualitative systematic reviews, mixed methods reviews and purpose-specific reviews. While this section is not intended to discuss the review families, we have provided a summary description of each review family and a diagram (Figure 4.1) that depicts the subcategories. For a more detailed read on these reviews, see the article “meeting the review family: exploring review types and associated information retrieval requirements” published by Sutton et al 2019.4
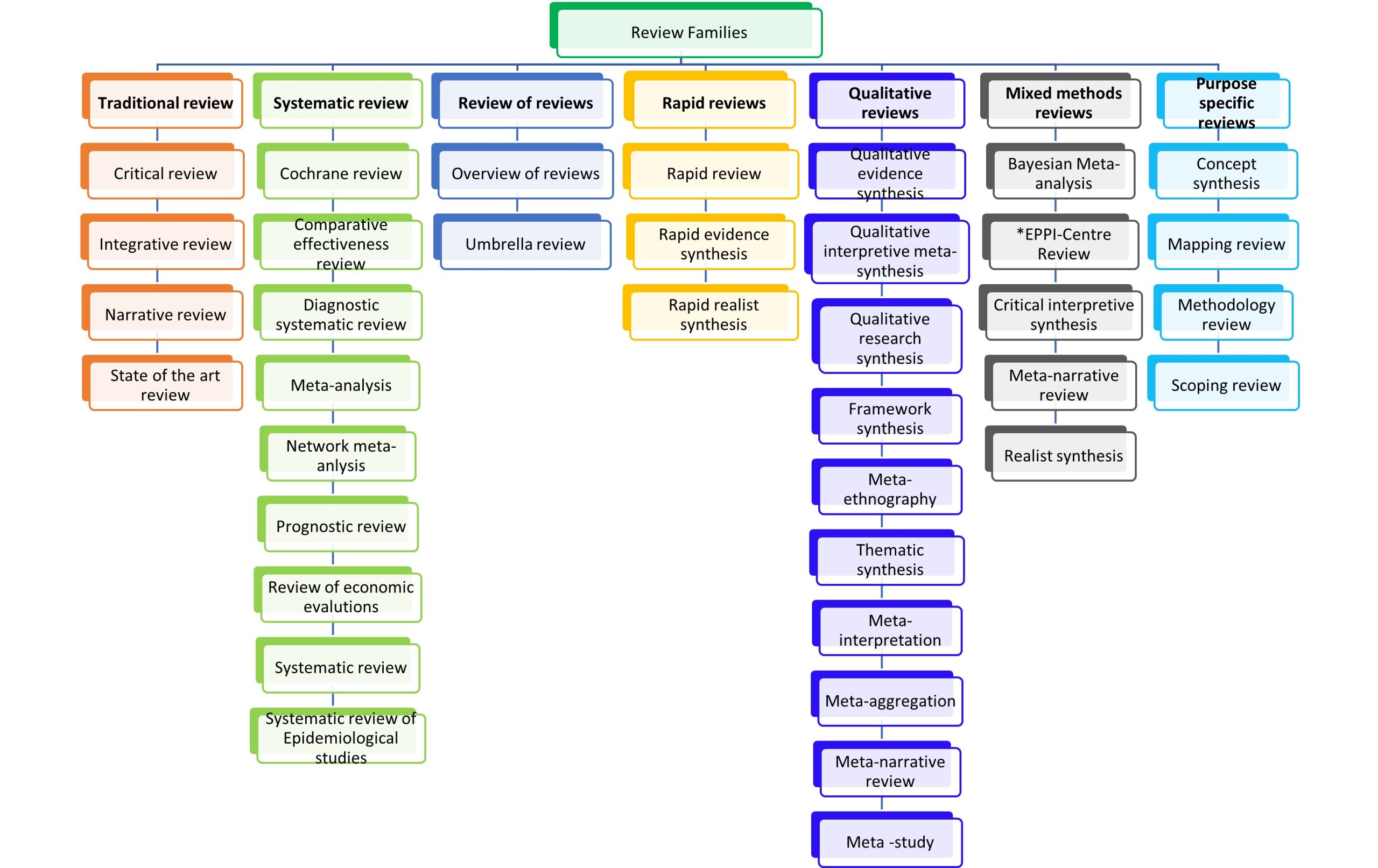
A detailed description of each major type of review is presented below.
NOW… Whether you are doing Professional or Research Honours, you will be doing a narrative or a scoping review.
Activity 1️⃣⏰20 Minutes
Chapter Attribution
Alele, F., & Malau-Aduli, B. (2023). An introduction to research methods for undergraduate health profession students. James Cook University. https://jcu.pressbooks.pub/intro-res-methods-health

