Overview
“A goal without a plan is just a wish.” ~ Larry Elder
and
“A plan without objectives is just an illusion.” ~ Associate Professor Carmen Reaiche
Disruptive events such as the COVID-19 pandemic has left organisations facing challenges to remain operative and economically efficient. Our current working environments are therefore characterised by a high degree of uncertainty and complexity. It is, in this precise time, that projects become a way to create benefits to businesses, and for project managers to embrace project management processes to deliver business value.
Projects are a normal, common activity in organisations. However, these are, in certain ways unique – by presenting different challenges, different types of work, and a demand for leadership. You can identify projects that involve a single unit of the business department as well as multiple departments. But regardless of the type of departments involved, projects are undertaken with a unique purpose: ‘to achieve specific and distinctive objectives.’
There are numerous examples of large, complex projects happening today (see Top 21 Projects Completing in 2021 ). You may be familiar with The West Side Project in Melbourne, the new Universal Studios project in Beijing, and our own James Cook University Technology Innovation Complex. One mega project I particularly like is The Elizabeth Tower of London restoration project, (Conservation of Elizabeth Tower and Big Ben ) also known as The Big Ben Makeover, costing approximately £80M (Inside Big Ben’s Makeover ). However, projects are not always large, nor are they all construction types. They may involve several factors: the relocation of offices, the development and launch of a new product or service, the design and implementation of new systems, processes, and procedures, or the conduct of a marketing event such as a sale, or new product promotion.
Most people in organisations are or will be involved in a project at some time. Project management is no longer considered a technical or specialised discipline (although some projects are very technical in nature). It is a different form of managing activities. Successful management of projects can not only assist the organisation to achieve its goals and objectives, but it can also help avoid considerable financial loss, waste, and duplication of effort and disruption. As such, knowledge of the principles and strategies of project management is a most useful asset for both managers and operators of organisations.
The past several decades have been marked by the rapid growth of project management in the government and private sector. Project management provides organisations with many skilled personnel, making Project Management a competitive and internationally accepted approach to doing business. Therefore, project management is no longer restricted to specialists. In fact, managing projects is often a vital part of everyone’s job. Evidence can be seen in the rapid shift to working remotely, which has caused a significant demand for project management skills. COVID-19 has imposed a shift on skills, requiring changes to the way we operate and often involving new business processes to remain effective. Project management skills are becoming part of the DNA of our own traits.
History
Could the Great Wall of China, the pyramids, or Stonehenge have been built without project management? It is possible to say that the concept of project management has been around since the beginning of history. It has enabled leaders to plan bold and massive projects and manage funding, materials, and labour within a designated time frame.
In the late 19th century, in the United States, large-scale government projects were the impetus for making important decisions that became the basis for project management methodology, such as the transcontinental railroad, which began construction in the 1860s. Suddenly, business leaders found themselves faced with the daunting task of organising the manual labour of thousands of workers and the processing and assembly of unprecedented quantities of raw material.
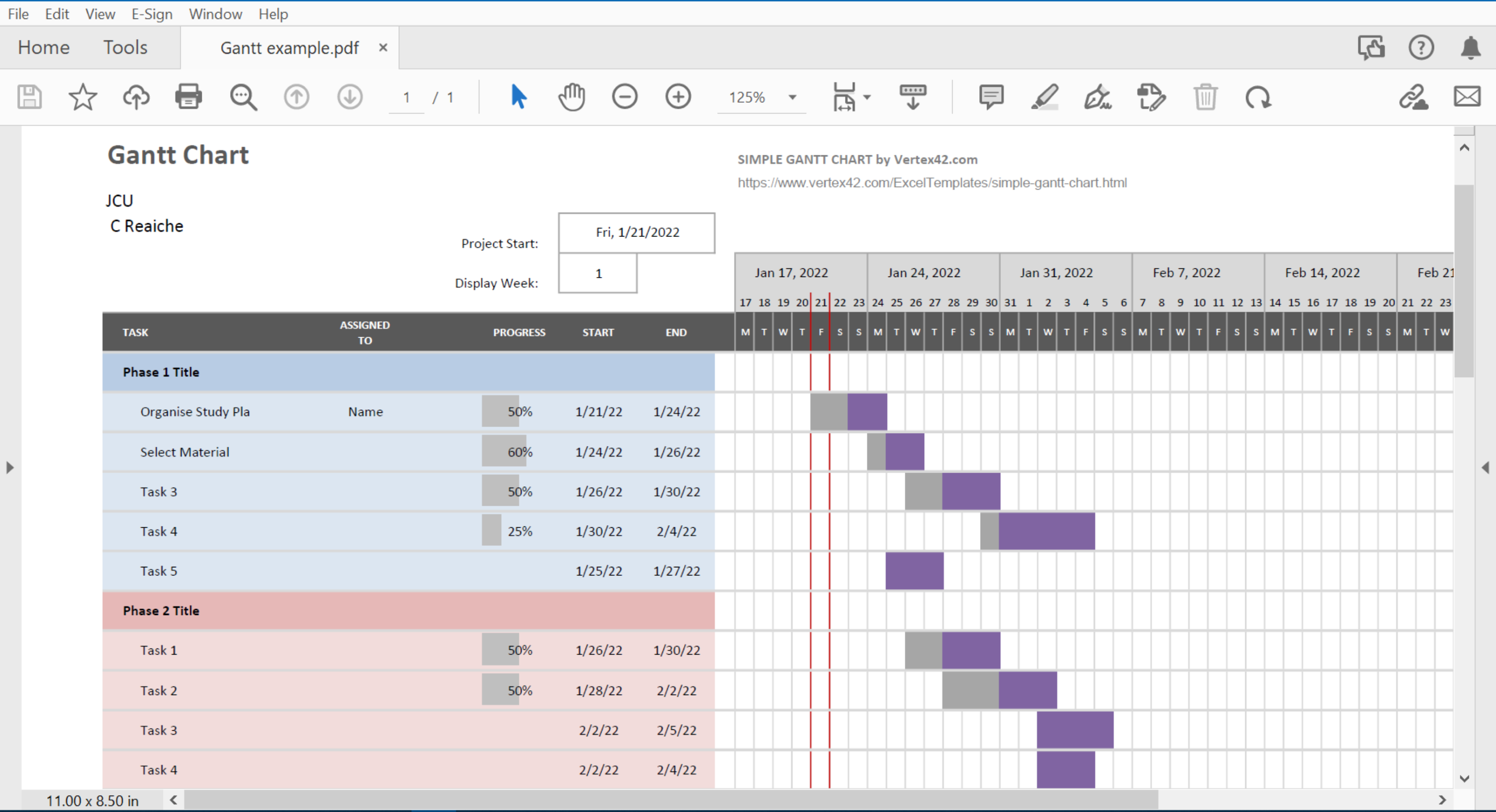
Henry Gantt, studied in great detail the order of operations in work and is most famous for developing the Gantt chart in the 1910s. A Gantt chart (as presented in the figure above) is a popular type of bar chart that illustrates a project schedule and has become a common technique for representing the phases and activities of a project so they can be understood by a wide audience. Although now a common charting technique, Gantt charts were considered revolutionary at the time they were introduced. Gantt charts were employed on major infrastructure projects in the United States, including the Hoover Dam and the interstate highway system and are still accepted today as important tools in project management.
By the mid-20th century, projects were managed on an ad hoc basis using mostly Gantt charts and informal techniques and tools. During that time, the Manhattan Project was initiated and its complexity was only possible because of project management methods. The Manhattan Project was the code name given to the Allied effort to develop the first nuclear weapons during World War II. It involved over 30 different project sites in the United States and Canada, and thousands of personnel from the United States, Canada, and the U.K. Born out of a small research program that began in 1939, the Manhattan Project would eventually employ 130,000 people, cost a total of nearly US$2 billion, and result in the creation of multiple production and research sites operated in secret. The project succeeded in developing and detonating three nuclear weapons in 1945.
The 1950s marked the beginning of the modern project management era. Two mathematical project-scheduling models were developed.
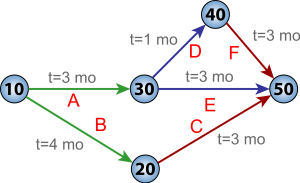
The program evaluation and review technique (PERT) was developed by Booz-Allen and Hamilton as part of the United States Navy’s Polaris missile submarine program. PERT is basically a method for analysing the tasks involved in completing a project, especially the time needed to complete each task, the dependencies among tasks, and the minimum time needed to complete the total project.
The critical path method (CPM) was developed in a joint venture by DuPont Corporation and Remington Rand Corporation for managing plant maintenance projects. The critical path determines the float, or schedule flexibility, for each activity by calculating the earliest start date, earliest finish date, latest start date, and latest finish date for each activity. The critical path is generally the longest full path on the project. Any activity with a float time that equals zero is considered a critical path task. CPM can help you figure out how long your complex project will take to complete and which activities are critical, meaning they have to be done on time or else the whole project will take longer. These mathematical techniques quickly spread into many private enterprises.
Project management in its present form began to take root a few decades ago. In the early 1960s, industrial and business organisations began to understand the benefits of organising work around projects. They understood the critical need to communicate and integrate work across multiple departments and professions.
Project Attributes
A project has distinctive attributes that distinguish it from ongoing work or business operations. Projects are temporary in nature. They are not an everyday business process and have definitive start dates and end dates. This characteristic is important because a large part of the project effort is dedicated to ensuring that the project is completed at the appointed time. To do this, schedules are created showing when tasks should begin and end. Projects can last minutes, hours, days, weeks, months, or years.
Projects exist to bring about a product or service that hasn’t existed before. In this sense, a project is unique. Unique means that this is new; this has never been done before. Maybe it’s been done in a very similar fashion before but never exactly in this way. For example, Ford Motor Company is in the business of designing and assembling cars. Each model that Ford designs and produces can be considered a project. The models differ from each other in their features and are marketed to people with various needs. An SUV serves a different purpose and clientele than a luxury car. The design and marketing of these two models are unique projects. However, the actual assembly of the cars is considered an operation (i.e., a repetitive process that is followed for most makes and models).
In contrast with projects, operations are ongoing and repetitive. They involve work that is continuous without an ending date and with the same processes repeated to produce the same results. The purpose of operations is to keep the organisation functioning while the purpose of a project is to meet its goals and conclude. Therefore, operations are ongoing while projects are unique and temporary.
A project is completed when its goals and objectives are accomplished. It is these goals that drive the project, and all the planning and implementation efforts undertaken to achieve them. Sometimes projects end when it is determined that the goals and objectives cannot be accomplished or when the product or service of the project is no longer needed, and the project is cancelled.
Definition of a Project
There are many written definitions of a project. All of them contain the key elements described above. For those looking for a formal definition of a project, the Project Management Institute (PMI) defines a project as a temporary endeavour undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result. The temporary nature of projects indicates a definite beginning and end. The end is reached when the project’s objectives have been achieved or when the project is terminated because its objectives will not or cannot be met, or when the need for the project no longer exists.
Project Characteristics
When considering whether or not you have a project on your hands, there are some things to keep in mind. First, is it a project or an ongoing operation? Second, if it is a project, who are the stakeholders? And third, what characteristics distinguish this endeavour as a project?
Projects have several characteristics:
- Projects are unique.
- Projects are temporary in nature and have a definite beginning and ending date.
- Projects are completed when the project goals are achieved or it’s determined the project is no longer viable.
A successful project is one that meets or exceeds the expectations of the stakeholders.
Consider the following scenario: The vice-president (VP) of marketing approaches you with a fabulous idea. (Obviously, it must be “fabulous” because he thought of it.) He wants to set up kiosks in local grocery stores as mini-offices. These offices will offer customers the ability to sign up for car and home insurance services as well as make their bill payments. He believes that the exposure in grocery stores will increase awareness of the company’s offerings. He told you that senior management has already cleared the project, and he’ll dedicate as many resources to this as he can. He wants the new kiosks in place in 12 selected stores in a major city by the end of the year. Finally, he has assigned you to head up this project.
Your first question should be, “Is it a project?” This may seem elementary, but confusing projects with ongoing operations happens often. Projects are temporary in nature, have definite start and end dates, result in the creation of a unique product or service, and are completed when their goals and objectives have been met and signed off by the stakeholders.
Using these criteria, let’s examine the assignment from the VP of marketing to determine if it is a project:
- Is it unique? Yes, because the kiosks don’t exist in the local grocery stores. This is a new way of offering the company’s services to its customer base. While the service the company is offering isn’t new, the way it is presenting its services is.
- Does the product have a limited time frame? Yes, the start date of this project is today, and the end date is the end of next year. It is a temporary endeavour.
- Is there a way to determine when the project is completed? Yes, the kiosks will be installed and the services will be offered from them. Once all the kiosks are installed and operating, the project will come to a close.
- Is there a way to determine stakeholder satisfaction? Yes, the expectations of the stakeholders will be documented in the form of requirements during the planning processes. These requirements will be compared to the finished product to determine if it meets the expectations of the stakeholder.
If the answer is yes to all these questions, then we have a project.
The Process of Project Management
You’ve determined that you have a project. What now? The notes you scribbled down on the back of the napkin at lunch are a start, but not exactly good project management practice. Too often, organisations follow Nike’s advice when it comes to managing projects when they “just do it.” An assignment is made, and the project team members jump directly into the development of the product or service requested. In the end, the delivered product doesn’t meet the expectations of the customer. Unfortunately, many projects follow this poorly constructed path, and that is a primary contributor to a large percentage of projects not meeting their original objectives, as defined by performance, schedule, and budget.
In Australia, more than 50 % of government projects appear to have failed and an estimate of only a 10% improvement appears to have been achieved in a total of 20 years. Unfortunately, many projects continue to show lack of good project management skills, tools application and governance. The 2013 Australian Government Infrastructure Department released a report of an Australian survey of Industry and Government senior executives that “found that on average 48% of projects failed to meet their baseline time, cost and quality objectives” (2013, p. 25).
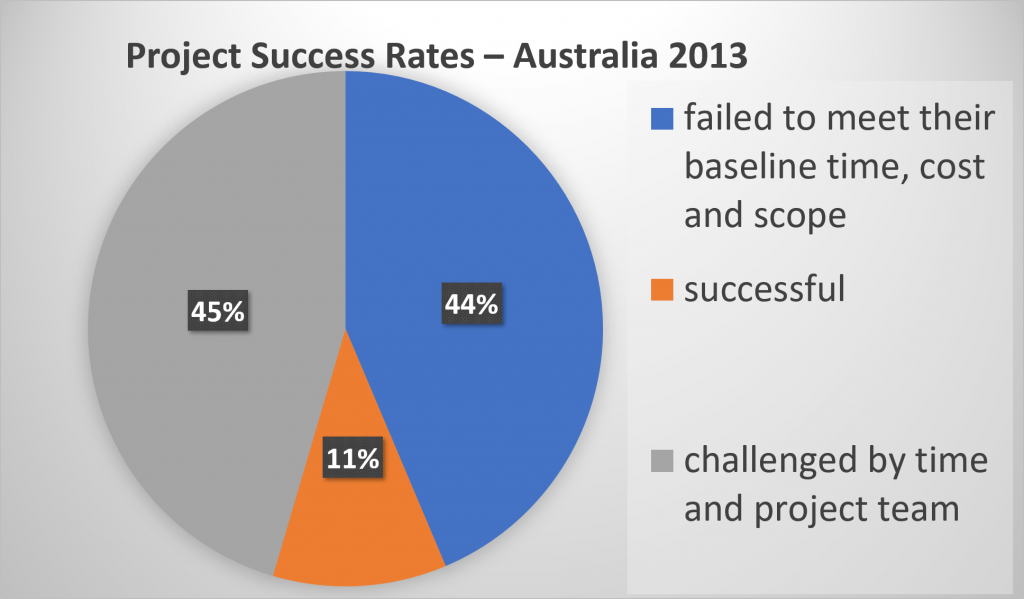
The figure above shows a summary of the 2013 infrastructure project’s outcome. You can access a detailed report at A Review of Project Governance Effectiveness In Australia
Applying good project management discipline is the way to help reduce these problems. Having good project management skills does not completely eliminate problems, risks, or surprises. The value of good project management is that you have standard processes in place to deal with all contingencies.
Project management is the application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques applied to project activities in order to meet the project requirements. Project management is a process that includes planning, putting the project plan into action, and measuring progress and performance.
Managing a project includes identifying your project’s requirements and writing down what everyone needs from the project. What are the objectives for your project? When everyone understands the goal, it’s much easier to keep them all on the right path. Make sure you set goals that everyone agrees on to avoid team conflicts later on. Understanding and addressing the needs of everyone affected by the project means the end result of your project is far more likely to satisfy your stakeholders. Last but not least, as project manager, you will also be balancing the many competing project constraints.
On any project, you will have a number of project constraints that are competing for your attention. They are cost, scope, quality, risk, resources, and time.
- Cost is the budget approved for the project, including all necessary expenses needed to deliver the project. Within organisations, project managers have to balance between not running out of money and not underspending because many projects receive funds or grants that have contract clauses with a “use it or lose it” approach to project funds. Poorly executed budget plans can result in a last-minute rush to spend the allocated funds. For virtually all projects, cost is ultimately a limiting constraint; few projects can go over budget without eventually requiring corrective action.
- Scope is what the project is trying to achieve. It entails all the work involved in delivering the project outcomes and the processes used to produce them. It is the reason and the purpose of the project.
- Quality is a combination of the standards and criteria to which the project’s products must be delivered for them to perform effectively. The product must perform to provide the functionality expected, solve the identified problem, and deliver the benefit and value expected. It must also meet other performance requirements, or service levels, such as availability, reliability, and maintainability, and have acceptable finish and polish. Quality on a project is controlled through quality assurance (QA), which is the process of evaluating overall project performance on a regular basis to provide confidence that the project will satisfy the relevant quality standards.
- Risk is defined by potential external events that will have a negative impact on your project if they occur. Risk refers to the combination of the probability the event will occur and the impact on the project if the event occurs. If the combination of the probability of the occurrence and the impact on the project is too high, you should identify the potential event as a risk and put a proactive plan in place to manage the risk.
- Resources are required to carry out the project tasks. They can be people, equipment, facilities, funding, or anything else capable of definition (usually other than labor) required for the completion of a project activity.
- Time is defined as the time to complete the project. Time is often the most frequent project oversight in developing projects. This is reflected in missed deadlines and incomplete deliverables. Proper control of the schedule requires the careful identification of tasks to be performed and accurate estimations of their duration, the sequence in which they are going to be done, and how people and other resources are to be allocated. Any schedule should take into account vacations and holidays.
You may have heard of the term “triple constraint,” which traditionally consisted of only time, cost, and scope. These are the primary competing project constraints that you have to be most aware of. The triple constraint is illustrated in the form of a triangle to visualise the project work and see the relationship between the scope/quality, schedule/time, and cost/resource. In this triangle, each side represents one of the constraints (or related constraints) wherein any changes to any one side cause a change in the other sides. The best projects have a perfectly balanced triangle. Maintaining this balance is difficult because projects are prone to change. For example, if the scope increases, cost and time may increase disproportionately. Alternatively, if the amount of money you have for your project decreases, you may be able to do as much, but your time may increase.
Your project may have additional constraints that you must face, and as the project manager, you have to balance the needs of these constraints against the needs of the stakeholders and your project goals. For instance, if your sponsor wants to add functionality to the original scope, you will very likely need more money to finish the project, or if they cut the budget, you will have to reduce the quality of your scope, and if you don’t get the appropriate resources to work on your project tasks, you will have to extend your schedule because the resources you have take much longer to finish the work.
You get the idea; the constraints are all dependent on each other. Think of all of these constraints as the classic carnival game of Whac-a-Mole. Each time you try to push one mole back in the hole, another one pops out. The best advice is to rely on your project team to keep these moles in place.
Project Management is continually improving the body of knowledge and developing extensions that define the differences in requirements and approaches for different kinds of projects, such as construction, new product development, and information systems in the Administrative Industry. Under the auspices of the Project Management Institute (Project Management Institute) and the Australian Institute of Project Management (AIPM), there is ongoing professional development and recognition of the value of project management to industry, government and other organisations.
Five volunteers founded the Project Management Institute (PMI) in 1969. Their initial goal was to establish an organisation where members could share their experiences in project management and discuss issues. Today, PMI is a non-profit project management professional association and the most widely recognised organisation in terms of promoting project management best practices. PMI was formed to serve the interests of the project management industry. The premise of PMI is that the tools and techniques of project management are common even among the widespread application of projects from the software to the construction industry. PMI first began offering the Project Management Professional (PMP) certification exam in 1984. Although it took a while for people to take notice, now more than 590,000 individuals around the world hold the PMP designation.
To help keep project management terms and concepts clear and consistent, PMI introduced the book A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) in 1987. It was updated it in 1996, 2000, 2004, 2009, 2013, 2017 and most recently in 2021 as the seventh edition. At present, there are more than four million copies of the PMBOK Guide in circulation. The highly regarded Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) has adopted it as its project management standard. In 1999, PMI was accredited as an American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standards developer and also has the distinction of being the first organisation to have its certification program attain International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 9001 recognition. In 2008, the organisation reported more than 650,000 members in over 213 countries and since then it has been recognised as the accreditation provider worldwide. PMI has its headquarters in Pennsylvania, United States, and also has offices in Washington, DC, and in Canada, Mexico, and China, as well as having regional service centres in Singapore, Brussels (Belgium), and New Delhi (India). Recently, an office was opened in Mumbai (India).
Because of the importance of projects, the discipline of project management has evolved into a working body of knowledge known as PMBOK – Project Management Body of Knowledge. The PMI is responsible for developing and promoting PMBOK. PMI also administers a professional certification program for project managers, the PMP. So if you want to get grounded in project management, PMBOK is the place to start, and if you want to make project management your profession, then you should consider becoming a PMP.
So what is PMBOK?
PMBOK is the fundamental knowledge you need for managing a project, categorised into 10 knowledge areas:
- Managing integration: Projects have all types of activities going on and there is a need to keep the “whole” thing moving collectively – integrating all of the dynamics that take place. Managing integration is about developing the project charter, scope statement, and plan to direct, manage, monitor, and control project change.
- Managing scope: Projects need to have a defined parameter or scope, and this must be broken down and managed through a work breakdown structure or WBS. Managing scope is about planning, definition, WBS creation, verification, and control.
- Managing time/schedule: Projects have a definite beginning and a definite ending date. Therefore, there is a need to manage the budgeted time according to a project schedule. Managing time/schedule is about definition, sequencing, resource and duration estimating, schedule development, and schedule control.
- Managing costs: Projects consume resources, and therefore, there is a need to manage the investment with the realisation of creating value (i.e., the benefits derived exceed the amount spent). Managing costs is about resource planning, cost estimating, budgeting, and control.
- Managing quality: Projects involve specific deliverables or work products. These deliverables need to meet project objectives and performance standards. Managing quality is about quality planning, quality assurance, and quality control.
- Managing human resources: Projects consist of teams and you need to manage project team(s) during the life cycle of the project. Finding the right people, managing their outputs, and keeping them on schedule is a big part of managing a project. Managing human resources is about human resources planning, hiring, and developing and managing a project team.
- Managing communication: Projects invariably touch lots of people, not just the end users (customers) who benefit directly from the project outcomes. This can include project participants, managers who oversee the project, and external stakeholders who have an interest in the success of the project. Managing communication is about communications planning, information distribution, performance reporting, and stakeholder management.
- Managing risk: Projects are a discovery-driven process, often uncovering new customer needs and identifying critical issues not previously disclosed. Projects also encounter unexpected events, such as project team members resigning, budgeted resources suddenly changing, the organisation becoming unstable, and newer technologies being introduced. There is a real need to properly identify various risks and manage these risks. Managing risk is about risk planning and identification, risk analysis (qualitative and quantitative), risk response (action) planning, and risk monitoring and control.
- Managing procurement: Projects procure the services of outside vendors and contractors, including the purchase of equipment. There is a need to manage how vendors are selected and managed within the project life cycle. Managing procurement is about acquisition and contracting plans, sellers’ responses and selections, contract administration, and contract closure.
- Managing stakeholders: Every project impacts people and organisations and is impacted by people and organisations. Identifying these stakeholders early, and as they arise and change throughout the project, is a key success factor. Managing stakeholders is about identifying stakeholders, their interest level, and their potential to influence the project; and managing and controlling the relationships and communications between stakeholders and the project.
This is the big framework for managing projects and if you want to be effective in managing projects, then you need to be effective in managing each of the 10 knowledge areas that make up PMBOK .
Certification in project management is available from the PMI, PRINCE2, ITIL, Critical Chain, and others. Agile project management methodologies (Scrum, extreme programming, Lean Six Sigma, others) also have certifications.
Careers Using Project Management Skills
Skills learned from your exposure to studying project management can be used in most careers as well as in your daily life. Strong planning skills, good communication, ability to implement a project to deliver the product or service while also monitoring for risks and managing the resources will provide an edge toward your success. Project managers can be seen in many industry sectors including agriculture and natural resources; arts, media, and entertainment; building trades and construction; energy and utilities; engineering and design; fashion and interiors; finance and business; health and human services; hospitality, tourism, and recreation; manufacturing and product development; public and private education services; public services; retail and wholesale trade; transportation; and information technology.
Below, we explore various careers and some of the ways in which project management knowledge can be leveraged.
Business Owners
Business owners definitely need to have some project management skills. With all successful businesses, the product or service being delivered to the customer meets their needs in many ways. The product or service is of the quality desired, the costs are aligned with what the consumer expected, and the timeliness of the product or service meets the deadline for the buyer of that item.
The pillars of project management are delivering a product/service within schedule, cost, scope, and quality requirements. Business owners need planning, organizing, and scoping skills and the ability to analyse, communicate, budget, staff, equip, implement, and deliver.
Understanding the finances, operations, and expenses of the business are among the skills that project managers learn and practice. Some businesses may focus more on accounting, providing financial advice, sales, training, public relations, and actuary or logistician roles. Business owners may own a travel agency or provide hospitality. Business owners could be managing a storefront or a location in their town’s marketplace.
Example: Restaurant Owner/Manager
Restaurant managers are responsible for the daily operations of a restaurant that prepares and serves meals and beverages to customers. Strong planning skills, especially coordinating with the various departments (kitchen, dining room, banquet operations, food service managers, vendors providing the supplies), ensure that customers are satisfied with their dining experience. Managers’ abilities to recruit and retain employees, and monitor employee performance and training, ensure quality with cost containment. Scheduling in many aspects, not only the staff but also the timing of the food service deliveries, is critical in meeting customer expectations.
Risk management is essential to ensure food safety and quality. Managers monitor orders in the kitchen to determine where delays may occur, and they work with the chef to prevent these delays. Legal compliance is essential in order for the restaurant to stay open, so restaurant managers direct the cleaning of the dining areas and the washing of tableware, kitchen utensils, and equipment. They ensure the safety standards and legality, especially in serving alcohol. Sensitivity and strong communication skills are needed when customers have complaints or employees feel pressured because more customers arrive than predicted.
Financial knowledge is needed for the soundness of running the restaurant, especially tracking special projects, events, and costs for the various menu selections. Catering events smoothly can be an outcome of using project plans and the philosophy of project management. The restaurant manager or the executive chef analyses the recipes to determine food, labour, and overhead costs; determines the portion size and nutritional content of each serving; and assigns prices to various menu items, so that supplies can be ordered and received in time.
Planning is the key to successful implementation. Managers or executive chefs need to estimate food needs, place orders with distributors, and schedule the delivery of fresh food and supplies. They also plan for routine services (equipment maintenance, pest control, waste removal) and deliveries, including linen services or the heavy cleaning of dining rooms or kitchen equipment, to occur during slow times or when the dining room is closed. A successful restaurant relies on many skills that the project management profession emphasises.
Outsourcing Services
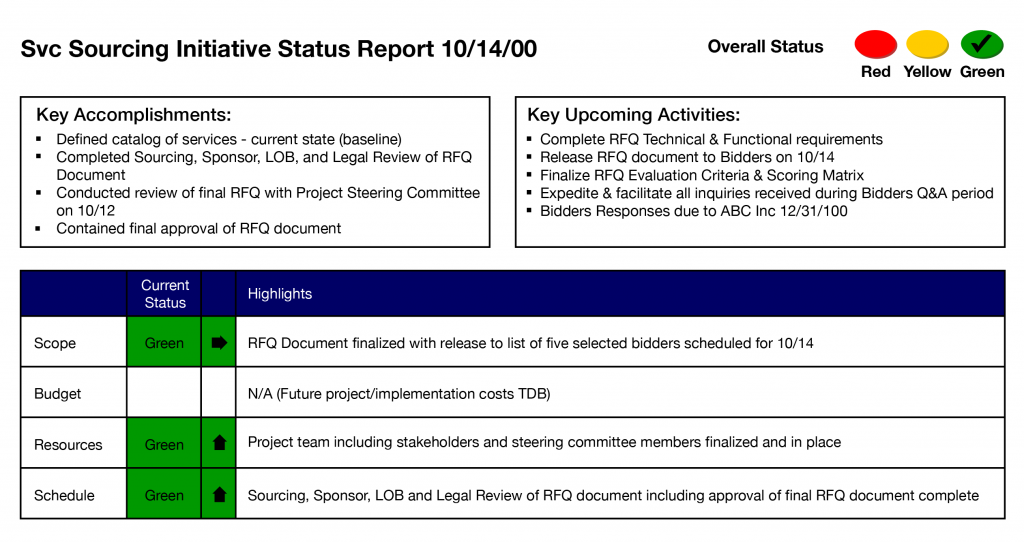
Many businesses explore outsourcing for certain services. Below is a sample status and project plan that reflects the various tasks needed for a project. A review of finances, the importance of communicating to stakeholders, and the importance of time, cost, schedule, scope, and quality are reflected. Many companies may use these steps in their business. These plans show the need for the entire team to review the various proposals to choose the best plan. The figure above represents a sample project status report.
Example: Construction Managers
Construction managers plan, direct, coordinate, and budget a wide variety of residential, commercial, and industrial construction projects, including homes, stores, offices, roads, bridges, wastewater treatment plants, schools, and hospitals. Strong scheduling skills are essential for this role. Communication skills are often used in coordinating design and construction processes, teams executing the work, and governance of special trades (carpentry, plumbing, electrical wiring) as well as government representatives for the permit processes.
A construction manager may be called a project manager or project engineer. The construction manager ensures that the project is completed on time and within budget while meeting quality specifications and codes and maintaining a safe work environment. These managers create project plans in which they divide all required construction site activities into logical steps, estimating and budgeting the time required to meet established deadlines, usually utilising sophisticated scheduling and cost-estimating software. Many use software packages such as Microsoft Project® or Procure® or online tools like BaseCamp®. Most construction projects rely on spreadsheets for project management. Procurement skills used in this field include acquiring the bills for material, lumber for the house being built, and more. Construction managers also coordinate labor, determining the needs and overseeing their performance, ensuring that all work is completed on schedule.
Values including sustainability, reuse, LEED-certified building, use of green energy, and various energy efficiencies are being incorporated into today’s projects with an eye to the future. Jennifer Russell spoke about project management and global sustainability at the 2011 Silicon Valley Project Management Institute (PMI) conference. She informed the attendees of the financial, environmental, and social areas in expanding the vision of project management with the slide in the figure below. These values are part of the PMI’s code of ethics and professionalism. By adhering to this code, project managers include in their decisions the best interests of society, the safety of the public, and enhancement of the environment.
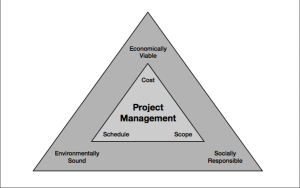
“Project Management Triangle” by Jennifer Russell is licensed under CC BY 3.0
Creative Services
Creative service careers include graphic artists, curators, video editors, gaming managers, multimedia artists, media producers, technical writers, interpreters, and translators. These positions use project management skills, especially in handling the delivery channel and meeting clients’ requirements.
Let us look at one example, graphic artists, to understand and identify some of the project management skills that aid in this career.
Example: Graphic Artists
Graphic artists plan, analyze, and create visual solutions to communication problems. They use many skills found in project management, especially communications. They work to achieve the most effective way to get messages across in print and electronic media. They emphasise their messages using colour, type, illustration, photography, animation, and various print and layout techniques. Results can be seen in magazines, newspapers, journals, corporate reports, and other publications. Other deliverables from graphic artists using project management skills include promotional displays, packaging, and marketing brochures supporting products and services, logos, and signage. In addition to print media, graphic artists create materials for the web, TV, movies, and mobile device apps.
Initiation in project management can be seen in developing a new design: determining the needs of the client, the message the design should portray, and its appeal to customers or users. Graphic designers consider cognitive, cultural, physical, and social factors in planning and executing designs for the target audience, very similar to some of the dynamics a project manager considers in communicating with various project stakeholders. Designers may gather relevant information by meeting with clients, creative staff, or art directors; brainstorming with others within their firm or professional association; and performing their own research to ensure that their results have high quality and they can manage risks.
Graphic designers may supervise assistants who follow instructions to complete parts of the design process. Therefore, scheduling, resource planning, and cost monitoring are pillars of project management seen in this industry. These artists use computers and communications equipment to meet their clients’ needs and business requirements in a timely and cost-efficient manner.
Educators
“Educator” is a broad term that can describe a career in teaching, maybe being a lecturer, a professor, a tutor, or a homeschooler. Other educators include gurus, mullahs, pastors, rabbis, and priests. Instructors also provide vocational training or teach skills like learning how to drive a car or use a computer. Educators provide motivation to learn a new language or showcase new products and services. Educators use project management skills, including planning and communication.
Let us look at teachers, since we all have had teachers, and see if we can recognise the project management skills that are demonstrated in this profession.
Example: Teachers
Some teachers foster the intellectual and social development of children during their formative years; other teachers provide knowledge, career skill sets, and guidance to adults. Project management skills that teachers exhibit include acting as facilitators or coaches and communicating in the classroom and in individual instruction. Project managers plan and evaluate various aspects of a project; teachers plan, evaluate, and assign lessons; implement these plans; and monitor each student’s progress similar to the way a project manager monitors and delivers goods or services. Teachers use their people skills to manage students, parents, and administrators. The soft skills that project managers exercise can be seen in teachers who encourage collaboration in solving problems by having students work in groups to discuss and solve problems as a team.
Project managers may work in a variety of fields with a broad assortment of people, similar to teachers who work with students from varied ethnic, racial, and religious backgrounds. These teachers must have awareness and understanding of different cultures.
Teachers in some schools may be involved in making decisions regarding the budget, personnel, textbooks, curriculum design, and teaching methods, demonstrating skills that a project manager would possess, such as financial management and decision making.
Engineers
Engineers apply the principles of science and mathematics to develop economical solutions to technical problems. As a project cycles from an idea in the project charter to the implementation and delivery of a product or service, engineers link scientific discoveries to commercial applications that meet societal and consumer needs.
Engineers use many project management skills, especially when they must specify functional requirements. They demonstrate attention to quality as they evaluate a design’s overall effectiveness, cost, reliability, and safety, similar to the project manager reviewing the criteria for the customer’s acceptance of delivery of the product or service.
Estimation skills in project management are used in engineering. Engineers are asked many times to provide an estimate of the time and cost required to complete projects.
Health Care
There are many jobs and careers in health care that use project management skills. Occupations in the field of health care vary widely, such as athletic trainer, dental hygienist, massage therapist, occupational therapist, optometrist, nurse, physician, physician assistant, and X-ray technician. These individuals actively apply risk management in providing health care delivery of service to their clients, ensuring that they do not injure the person they are caring for. Note: There is a section on nursing later in this chapter.
Many of you may have had a fall while you were growing up, and needed an X-ray to determine if you had a fracture or merely a sprain. Let us look at this career as an example of a health care professional using project management skills.
Example: Radiology Technologists
Radiology technologists and technicians perform diagnostic imaging examinations like X-rays, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and mammography. They could also be called radiographers, because they produce X-ray films (radiographs) of parts of the human body for use in diagnosing medical problems.
Project management skills, especially people skills and strong communication, are demonstrated when they prepare patients for radiologic examinations by explaining the procedure and what position the patient needs to be in, so that the parts of the body can be appropriately radiographed. Risk management is demonstrated when these professionals work to prevent unnecessary exposure to radiation by surrounding the exposed area with radiation protection devices, such as lead shields, or limiting the size of the X-ray beam. To ensure quality results, the health technician monitors the radiograph and sets controls on the X-ray machine to produce radiographs of the appropriate density, detail, and contrast.
Safety and regulations concerning the use of radiation to protect themselves, their patients, and their coworkers from unnecessary exposure is tracked in an efficient manner and reported as a control to ensure compliance. Project management skills are also used in preparing work schedules, evaluating equipment for purchase, or managing a radiology department.
Some radiological technologists specialise in CT scans; as CT technologists they too use project management skills. CT uses ionizing radiation to produce a substantial number of cross-sectional X-rays of an area of the body. Therefore, it requires the same precautionary measures that are used with X-rays, hence the need for risk management and monitoring for exposure.
Teamwork, not only with the patient that the radiologist technologist supports and the doctor who ordered the request, but also with other health care providers, relies on strong communication, quality, work done in a timely manner, and wise use of hospital resources. This all boils down to ensuring that the three elements of the project management triangle of cost, schedule, and scope, with quality delivered remain the essentials that provide a cornerstone to project management and the skills needed to obtain the objective.
Example: Nurses
Nurses treat and educate patients and their families and the public about various medical conditions and provide advice and emotional support. Nurses establish a care plan for their patients that include activities like scheduling the administration and discontinuation of medications (e.g., intravenous (IV) lines for fluid, medication, blood, and blood products) and application of therapies and treatments. Communication with the patient, their family, physicians and other health care clinicians may be done in person or via technology. Telehealth allows nurses to provide care and advice through electronic communications media including videoconferencing, the Internet, or telephone.
Risk management is very important for a nurse, with some cases having a life or death consequence. Nurses monitor pain management and vital signs and provide status reports to physicians to help in responding to the health care needs of the patient.
The nursing field varies. Some nurses work in infection control. They identify, track, and control infectious outbreaks in health care facilities and create programs for outbreak prevention and response to biological terrorism. Others are educators who plan, develop, execute, and evaluate educational programs and curricula for the professional development of students and graduate nurses. Nurses may use project management skills while conducting health care consultations, advising on public policy, researching in the field, or providing sales support of a product or service.
Paralegal
Attorneys assume the ultimate responsibility for legal work but they often obtain assistance. Paralegals assume this role in law firms and perform many tasks to aid the legal profession. However, they are explicitly prohibited from carrying out duties considered to be the practice of law (e.g., giving legal advice, setting legal fees, presenting court cases).
Project management skills, such as planning, are used in helping lawyers prepare for closings, hearings, trials, and corporate meetings. Communication skills are used in preparing written reports that help attorneys determine how cases should be handled or drafts for actions such as pleading, filing motions, and obtaining affidavits.
Monitoring skills aid paralegals who may track files of important case documents, working on risk containment related to filing dates and responses to the court. Procurement skills, which a project manager uses, can also be seen from a paralegal perspective in negotiating terms of hiring expert witnesses ,as well as other services such as acquiring services from process servers.
Financial skills may be used as well, such as assisting in preparing tax returns, establishing trust funds, and planning estates or maintaining financial office records at the law firm.
Government, litigation, personal injury, corporate law, criminal law, employee benefits, intellectual property, labour law, bankruptcy, immigration, family law, and real estate are some of the many different law practices where a paralegal professional may use project management skills.
Software developer
Computer software developers and computer programmers design and develop software. They apply the principles of computer science and mathematics to create, test, and evaluate software applications and systems that make computers come alive. Software is developed in many kinds of projects: computer games, business applications, operating systems, network control systems, and more. Software developers use project management skills to develop the requirements for the software, identify and track the product development tasks, communicate within the development team and with clients, test cases, and manage quality, the schedule, and resources (staff, equipment, labs, and more).
Science Technicians
Science technicians use principles and theories of science and mathematics to assist in research and development and help invent and improve products and processes. In their jobs, they are more practically oriented than scientists. Planning skills project managers use can be seen as science technicians set up, operate, and maintain laboratory instruments; monitor experiments; and observe, calculate, and record results. Quality is a factor here as it is in project management; science technicians must ensure that processes are performed correctly, with proper proportions of ingredients, for purity or for strength and durability.
There are different fields in which science technicians can apply project management skills. Agricultural and food science technicians test food and other agricultural products and are involved in food, fibre, and animal research, production, and processing. Control and risk management are important here in executing the tests and experiments, for example, to improve the yield and quality of crops, or the resistance of plants and animals to disease, insects, or other hazards. Quality factors are paramount when food science technicians conduct tests on food additives and preservatives to ensure compliance with government regulations regarding colour, texture, and nutrients.
Biological technicians work with biologists studying living organisms. Many assist scientists who conduct medical research or who work in pharmaceutical companies to help develop and manufacture medicines. Skills in scheduling, especially in incubation periods for the study of the impact on cells, could impact projects, such as exploring and isolating variables for research in living organisms and infectious agents. Biotechnology technicians apply knowledge and execution skills and techniques gained from basic research, including gene splicing and recombinant DNA, to product development. Project management skills are used in collaboration and communication among team members to record and understand the results and progress toward a cure or product.
Other kinds of technicians are chemical technicians who may work in laboratories or factories, using monitoring and control skills in the way they collect and analyse samples. Again, quality assurance is an important factor for most process technicians’ work in manufacturing, testing, packaging for design, ensuring the integrity of materials, and verifying environmental acceptability.
Technicians use a project management skill set to assist in their initiation, planning, and executing tasks, while managing risks with some measure of reporting to determine if their objectives satisfy the constraints of cost, schedule, resource, and quality standards set.
Text Attributions
This section contains material derived and remixed from the following sources:
- Project Management – 2nd Edition by Adrienne Watt is licensed under CC BY (Attribution) 4.0 International License
- Project Management by Merrie Barron and Andrew Barron is licensed under CC BY (Attribution) 3.0
- Project Management for Skills for All Careers by Project Management Open Resources and TAP-a-PM is licensed under CC BY (Attribution) 3.0

