3.2 Quantitative Research Designs
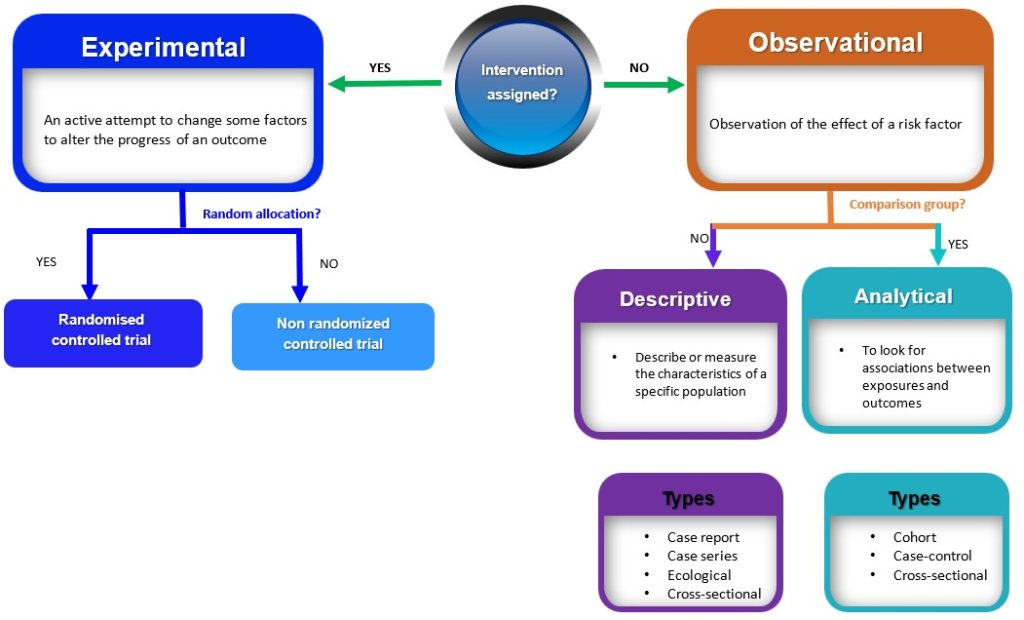
Quantitive research study designs can be broadly classified into two main groups (observational and experimental) depending on if an intervention is assigned. If an intervention is assigned, then an experimental study design will be considered; however, if no intervention is planned or assigned, then an observational study will be conducted. 3 These broad classes are further subdivided into specific study designs, as shown in Figure 3.1. In practice, quantitative studies usually begin simply as descriptive studies, which could subsequently be progressed to more complex analytic studies and then to experimental studies where appropriate.
Observational studies
Observational studies are research designs that involve observing and measuring the characteristics of a sample or population without intervening, altering or manipulating any variables (Figure 3.1). 3 Observational studies can be further subdivided into descriptive and analytic studies. 3
Descriptive observational studies
Descriptive studies are research designs that describe or measure the characteristics of a specific population or phenomenon. These characteristics include descriptions related to the phenomenon under investigation, the people involved, the place, and the time. 4 These study designs are typically non-experimental and do not involve manipulating variables; rather, they rely on the collection and analysis of numerical data to draw conclusions. Examples of descriptive studies include case reports, case series, ecological studies and cross-sectional (prevalence studies). 2 These are discussed below
- Case Reports and Case series
Case reports and case series are both types of descriptive studies in research. A case report is a detailed account of the medical history, diagnosis, treatment, and outcome of a single patient. 5 On the other hand, case series is a collection of cases with similar clinical features. 5 Case series are frequently used to explain the natural history of a disease, the clinical characteristics, and the health outcomes for a group of patients who underwent a certain treatment. Case series typically involve a larger number of patients than case reports. 5 Both case reports and case series are used to illustrate unusual or atypical features found in patients in practice. 5 In a typical, real-world clinical situation, they are both used to describe the clinical characteristics and outcomes of individual patients or a group of patients with a particular condition. These studies have the potential to generate new research questions and ideas. 5 However, there are drawbacks to both case reports and case series, such as the absence of control groups and the potential for bias. Yet, they can be useful sources of clinical data, particularly when researching uncommon or recently discovered illnesses. 5 An example of a case report is the study by van Tulleken, Tipton and Haper, 2018 which showed that open-water swimming was used as a treatment for major depressive disorder for a 24-year-old female patient.6 Weekly open (cold) water swimming was trialled, leading to an immediate improvement in mood following each swim. A sustained and gradual reduction in symptoms of depression, and consequently a reduction in, and cessation of, medication was observed.6 An example of a case series is the article by Chen et al, 2020 which described the epidemiology and clinical characteristics of COVID-19 infection among 12 confirmed cases in Jilin Province, China.7
- Ecological studies
Ecological studies examine the relationship between exposure and outcome at the population level. Unlike other epidemiological studies focusing on individual-level data, ecological studies use aggregate data to investigate the relationship between exposure and outcome of interest. 8 In ecological studies, data on prevalence and the degree of exposure to a given risk factor within a population are typically collected and analysed to see if exposure and results are related. 8 Ecological studies shed light on the total burden of disease or health-related events within a population and assist in the identification of potential risk factors that might increase the incidence of disease/event. However, these studies cannot prove causation or take into account characteristics at the individual level that can influence the connection between exposure and result. This implies that ecological findings cannot be interpreted and extrapolated to individuals. 9 For example, the association between urbanisation and Type 2 Diabetes was investigated at the country level, and the role of intermediate variables (physical inactivity, sugar consumption and obesity) was examined. One of the key findings of the study showed that in high-income countries (HIC), physical inactivity and obesity were the main determinants of T2D prevalence.10 However, it will be wrong to infer that people who are physically inactive and obese in HIC have a higher risk of T2D.
- Cross-sectional Descriptive (Prevalence) studies
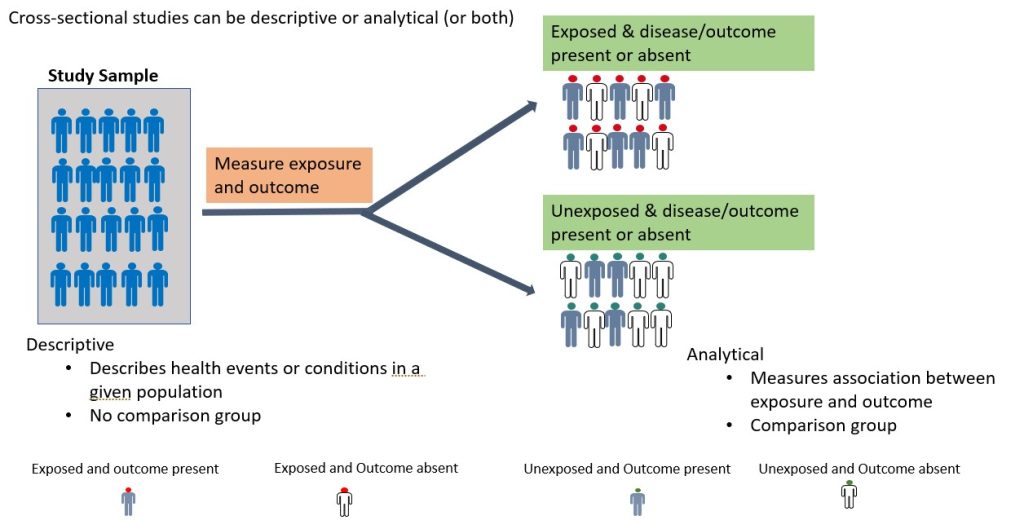
A cross-sectional study is an observational study in which the researcher collects data on a group of participants at a single point in time. 11 The goal is to describe the characteristics of the group or to explore relationships between variables. Cross-sectional studies can be either descriptive or analytical (Figure 3.2). 11 Descriptive cross-sectional studies are also known as prevalence studies measuring the proportions of health events or conditions in a given population. 11 Although analytical cross-sectional studies also measure prevalence, however, the relationship between the outcomes and other variables, such as risk factors, is also assessed. 12 The main strength of cross-sectional studies is that they are quick and cost-effective. However, they cannot establish causality and may be vulnerable to bias and confounding (these concepts will be discussed further later in this chapter under “avoiding error in quantitative research). An example of a cross-sectional study is the study by Kim et al., 2020 which examined burnout and job stress among physical and occupational therapists in various Korean hospital settings. 13 Findings of the study showed that burnout and work-related stress differed significantly based on several factors, with hospital size, gender, and age as the main contributory factors. The more vulnerable group consisted of female therapists in their 20s at small- or medium-sized hospitals with lower scores for quality of life. 13
Analytical Observational studies
Analytical observational studies aim to establish an association between exposure and outcome and identify causes of disease (causal relationship). 14 Analytical observational studies include analytical cross-sectional (discussed above), case-control and cohort studies. 14 This research method could be prospective(cohort study) or retrospective (case-control study), depending on the direction of the enquiry. 14
- Case-control studies
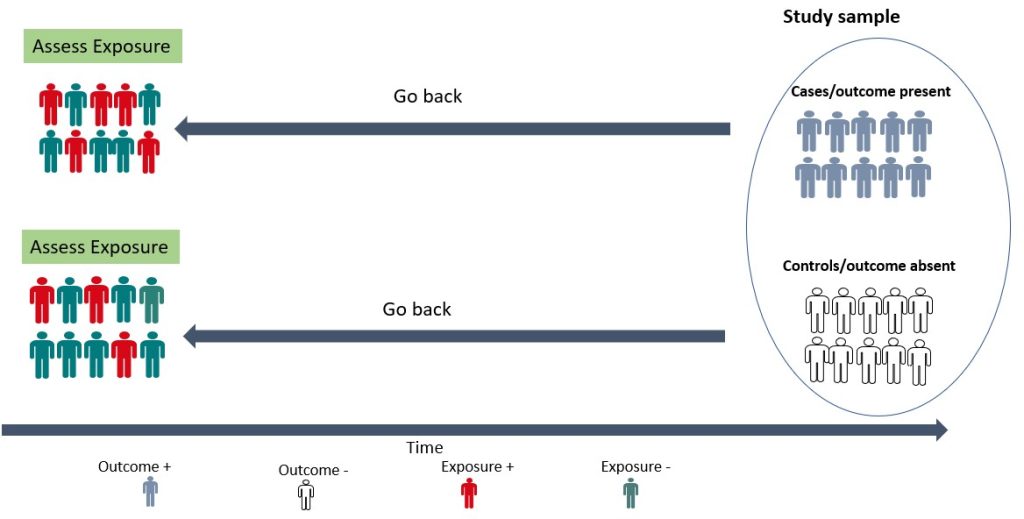
A case-control study is a retrospective study in which the researcher compares a group of individuals with a specific outcome (cases) to a group of individuals without that outcome (controls) to identify factors associated with the outcome. 15 As shown in Figure 3.3 below, the cases and controls are recruited and asked questions retrospectively (going back in time) about possible risk factors for the outcome under investigation. A case-control study is relatively efficient in terms of time, money and effort, suited for rare diseases or outcomes with a long latent period, and can examine multiple risk factors. 15 For example, before the cause of lung cancer, was established, a case-control study was conducted by British researchers Richard Doll and Bradford Hill in 1950. 16 Subjects with lung cancer were compared with those who did not have lung cancer, and details about their smoking habits were obtained. 16 The findings from this initial study showed that cancer patients were more frequent and heavy smokers. 16 Over the years, more evidence has been generated implicating tobacco as a significant cause of lung cancer. 17, 18 Case-control studies are, therefore, useful for examining rare outcomes and can be conducted more quickly and with fewer resources than other study designs. Nonetheless, it should be noted that case-control studies are susceptible to bias in selecting cases and controls and may not be representative of the overall population. 15
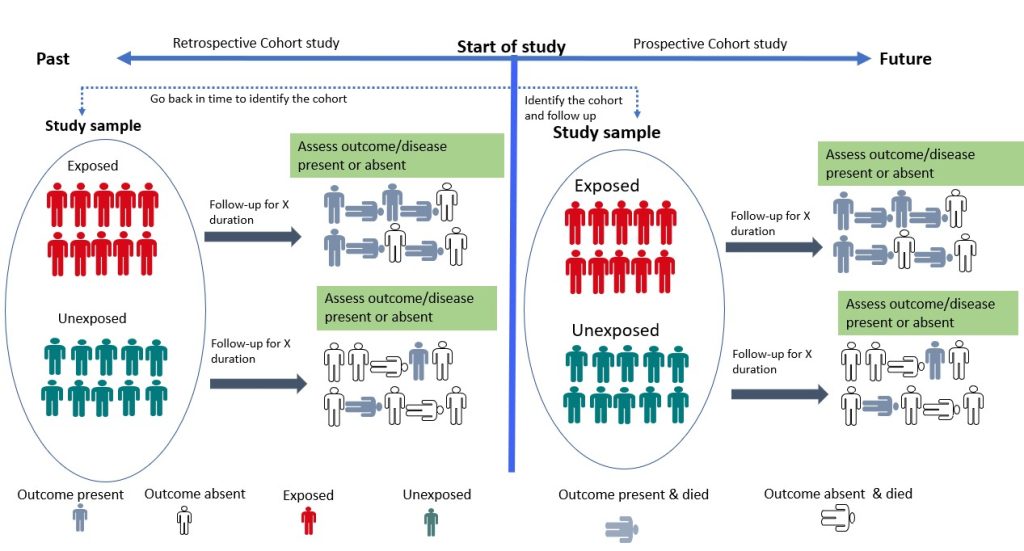
- Cohort Study
Cohort studies are longitudinal studies in which the researcher follows a group of individuals who share a common characteristic (e.g., age, occupation) over time to monitor the occurrence of a particular health outcome. 19 The study begins with the selection of a group of individuals who are initially free of the disease or health outcome of interest (the “cohort”). The cohort is then divided into two or more groups based on their level of exposure (for example, those who have been exposed to a certain risk factor and those who have not). 19 Participants are then followed up, and their health outcomes are tracked over time. The incidence of the health outcome is compared between exposed and non-exposed groups, and the relationship between exposure and the outcome is quantified using statistical methods. 19 Cohort studies can be prospective or retrospective (Figure 3.4). 20 In a prospective cohort study, the researchers plan the study so that participants are enrolled at the start of the study and followed over time. 20, 21 In a retrospective cohort study, data on exposure and outcome are collected from existing records or databases. The researchers go back in time (via available records) to find a cohort that was initially healthy and “at risk” and assess each participant’s exposure status at the start of the observation period. 20, 21 Cohort studies provide an understanding of disease risk factors based on findings in thousands of individuals over many years and are the foundation of epidemiological research. 19 They are useful for investigating the natural history of a disease, identifying risk factors for a disease, providing strong evidence for causality and estimating the incidence of a disease or health outcome in a population. However, they can be expensive and time-consuming to conduct. 15 An example of a cohort study is the study by Watts et al, 2015 which investigated whether the communication and language skills of children who have a history of stuttering are different from children who do not have a history of stuttering at ages 2–5 years. 22 The findings revealed that children with a history of stuttering, as a group, demonstrated higher scores on early communication and language measures compared to their fluent peers. According to the authors, clinicians can be reassured by the finding that, on average, children who stutter have early communication and language skills that meet developmental expectations. 22
Experimental Study Designs (Interventional studies)
Experimental studies involve manipulating one or more variables in order to measure their effects on one or more outcomes. 23 In this type of study, the researcher assigns individuals to two or more groups that receive or do not receive the intervention. Well-designed and conducted interventional studies are used to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables. 23 Experimental studies can be broadly classified into two – randomised controlled trials and non-randomised controlled trials. 23 These study designs are discussed below:
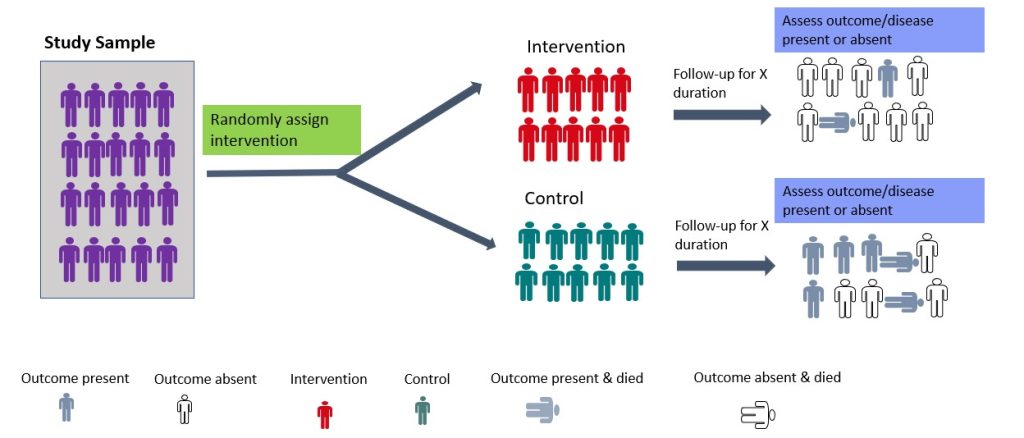
- Randomised Controlled Trial
Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) are experimental studies in which participants are randomly assigned to the intervention or control arm of the study. 23 The experimental group receives the intervention, while the control group does not (Figure 3.5). RCTs involve random allocation (not by choice of the participants or investigators) of participants to a control or intervention group (Figure 3.5). 24 Randomization or random allocation minimises bias and offers a rigorous method to analyse cause-and-effect links between an intervention and outcome. 24 Randomization balances participant characteristics (both observed and unobserved) between the groups. 24 This is so that any differences in results can be attributed to the research intervention. 24 The most basic form of randomisation is allocating treatment by tossing a coin. Other methods include using statistical software to generate random number tables and assigning participants by simple randomisation or allocating them sequentially using numbered opaque envelopes containing treatment information. 25 This is why RCTs are often considered the gold standard in research methodology. 24 While RCTs are effective in establishing causality, they are not without limitations. RCTs are expensive to conduct and time-consuming. In addition, ethical considerations may limit the types of interventions that can be tested in RCTs. They may also not be appropriate for rare events or diseases and may not always reflect real-world situations, limiting their application in clinical practice. 24 An example of a randomised controlled trial is the study by Shebib et al., 2019 which investigated the effect of a 12-week digital care program (DCP) on improving lower-back pain. The treatment group (DCP) received the 12-week DCP, consisting of sensor-guided exercise therapy, education, cognitive behavioural therapy, team and individual behavioural coaching, activity tracking, and symptom tracking – all administered remotely via an app. 26 While the control group received three digital education articles only. The findings of the study showed that the DCP resulted in improved health outcomes compared to treatment-as-usual and has the potential to scale personalised evidence-based non-invasive treatment for patients with lower-back pain. 26
- Non-randomised controlled design (Quasi-experimental)
Non-randomised controlled trial (non-RCT) designs are used where randomisation is impossible or difficult to achieve. This type of study design requires allocation of the exposure/intervention by the researcher. 23 In some clinical settings, it is impossible to randomise or blind participants. In such cases, non-randomised designs are employed. 27 Examples include pre-posttest design (with or without controls) and interrupted time series. 27, 28 For the pre-posttest design that involves a control group, participants (subjects) are allocated to intervention or control groups (without randomisation) by the researcher. 28 On the other hand, it could be a single pre-posttest design study where all subjects are assessed at baseline, the intervention is given, and the subjects are re-assessed post-intervention. 28 An example of this type of study was reported by Lamont and Brunero (2018), who examined the effect of a workplace violence training program for generalist nurses in the acute hospital setting. The authors found a statistically significant increase in behaviour intention scores and overall confidence in coping with patient aggression post-test. 29 Another type of non-RCT study is the interrupted time series (ITS) in which data are gathered before and after intervention at various evenly spaced time points (such as weekly, monthly, or yearly). 30 Thus, it is crucial to take note of the precise moment an intervention occurred. The primary goal of an interrupted time series is to determine whether the data pattern observed post-intervention differs from that noted prior. 30 Several ITS were conducted to investigate the effectiveness of the different prevention strategies (such as lockdown and border closure) used during the COVID pandemic. 31, 32 Although non-RCT may be more feasible to RCTs, they are more prone to bias than RCTs due to the lack of randomisation and may not be able to control for all the variables that might affect the outcome. 23
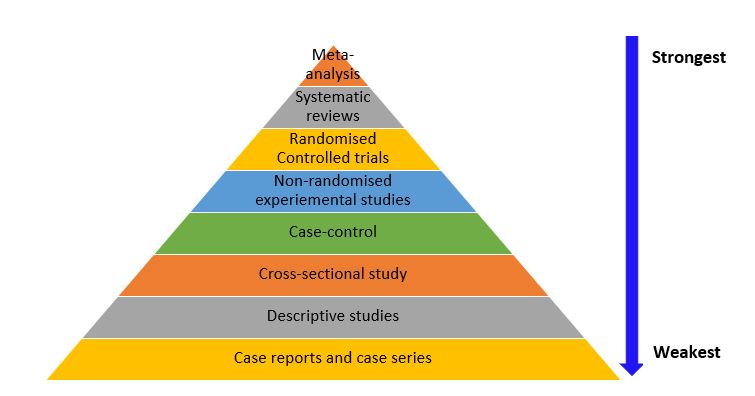
Hierarchy of Evidence
While each study design has its unique characteristics and strengths, they are not without weaknesses (as already discussed) that impact the accuracy of the results and research evidence they provide. The hierarchy of evidence is a framework used to rank the evidence provided by different study designs in research evaluating healthcare interventions with respect to the strength of the presented results (i.e., validity and reliability of the findings). 33 Study designs can be ranked in terms of their ability to provide valid evidence on the effectiveness (intervention achieves the intended outcomes), appropriateness (impact of the intervention from the perspective of its recipient) and feasibility (intervention is implementable) of the research results they provide. 33 As shown in Figure 3.6, meta-analyses, systematic reviews, and RCTs provide stronger best-practice evidence and scientific base for clinical practice than descriptive studies as well as case reports and case series. Nonetheless, it is important to note that the research question/ hypothesis determines the study design, and not all questions can be answered using an interventional design. In addition, there are other factors that need to be considered when choosing a study design, such as funding, time constraints, and ethical considerations, and these factors are discussed in detail in chapter 6.